About the Parish Council
Powers and Duties Of Parish Councils
The Parish Council is the first tier of local government for East Woodhay. The Council consists of 10 councillors who are elected every four years by the residents to represent their interests.
Parish Councils have a wide range of powers and duties.
In Hampshire, as in other parts of the UK, the roles of parish councils, town councils, borough councils, and county councils differ based on the levels of local government they represent and their respective responsibilities. Here’s an overview of each:
Parish Council
-
Scope: The most local form of government, typically serving small rural or suburban areas.
-
Responsibilities:
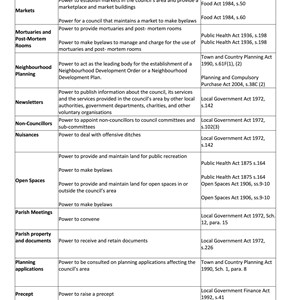
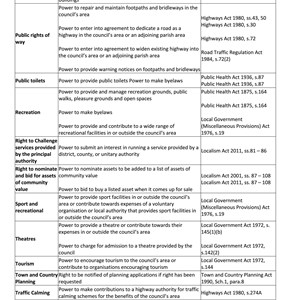
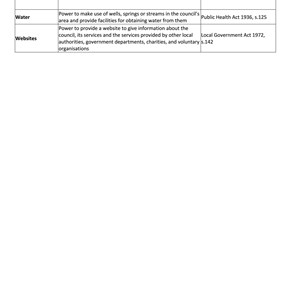
- Local amenities: Parish councils often manage and maintain local community spaces such as parks, village halls, cemeteries, and playing fields.
- Community activities: They may support or organize local events, activities, and initiatives.
- Consultation with residents: Parish councils act as a point of contact for residents, often organizing consultations on local issues or concerns.
- Planning matters: They can be consulted on planning applications within their area but have no decision-making power; their role is advisory.
- Local projects: Some parish councils manage small-scale local services, such as bus shelters, street lighting, or local grants for community projects.
-
Funding: Primarily funded by a local precept (a tax levied on the residents) and sometimes grants or other funding sources.
-
Representation: Composed of locally elected councillors, typically referred to as parish or town councillors. These councils are often non-partisan.
Town Councils
-
Scope: A town council operates in a larger urban area than a parish council, but its responsibilities are similar, with a focus on the local community.
-
Responsibilities:
- Similar to Parish Councils: Town councils have similar duties to parish councils but may manage more significant community assets such as town centers, markets, and larger public events.
- Local Services: They may run or contribute to local services like public toilets, local markets, and public transport subsidies.
- Civic Leadership: Town councils often take on a role of civic pride, hosting events such as town festivals, Remembrance Day services, and local commemorations.
-
Funding: They are funded through the local precept (a local tax) and may also receive grants and contributions from higher levels of government.
Borough Councils (Basingstoke and Deane Borough Council)
-
Scope: A borough council covers a larger area than a parish or town council, and it serves a more urbanized area, typically consisting of several towns or villages.
-
Responsibilities:
- Local Governance: Borough councils are responsible for a wide range of local services and functions such as waste collection, housing, social services, local planning, environmental health, leisure services, and public health.
- Planning and Development: Borough councils have significant powers to make decisions on planning applications, building regulations, and local infrastructure development.
- Economic Development: They focus on encouraging local business, creating job opportunities, and managing town regeneration projects.
- Education: While education is largely managed by County Councils, borough councils might support schools in terms of facilities and may also be involved in local youth services and community education programs.
-
Funding: Funded by council tax (from residents), government grants, and income from services or business rates. Borough councils are often responsible for the collection of business rates in their areas.
-
Representation: Borough councils are made up of elected councillors who represent individual wards or districts within the borough. The council is typically led by a mayor or leader, and often operates within a political party framework.
County Councils (Hampshire County Council)
-
Scope: The highest level of local government in the area, responsible for a large geographical region, typically covering several boroughs, towns, and parishes.
-
Responsibilities:
- Strategic Services: County councils manage larger services such as education (through schools, school transport, and adult education), transport (including roads, highways, and public transportation), social services (adult and children's services, including care for the elderly and vulnerable people), and public health.
- Countywide Planning: The county council deals with strategic planning issues, such as regional infrastructure, waste management (e.g., recycling and landfill), and managing large-scale environmental projects.
- Emergency Services: They have a role in coordinating emergency services, working with the police, fire, and ambulance services for disaster preparedness and response.
- Environmental Management: County councils oversee large-scale environmental management, including conservation projects, climate change initiatives, and waste recycling.
-
Funding: Funded by council tax (from residents across the county), government grants, and business rates. They also receive specific funding for some services, like education or transport.
-
Representation: County councils are made up of elected county councillors, who represent specific electoral divisions (usually smaller than boroughs but larger than individual wards in towns or parishes). The council is typically led by a council leader, and the political party in control will influence policy direction.
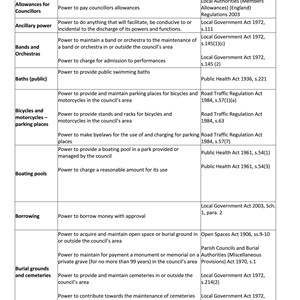
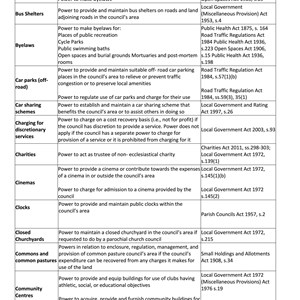
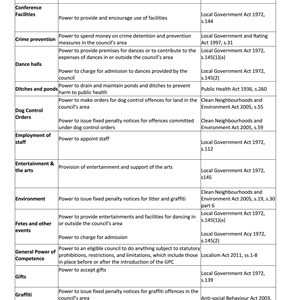
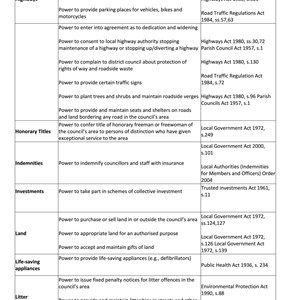
The following tables describe the powers and duties held by local councils for a number of functions. It also provides details of the regulations under which statutory provisions are made.